Infrared Applications in the Power Industry
Maintaining power equipment without interruption is crucial for ensuring system reliability and safety. Traditional inspection methods often fail to detect equipment deterioration and thermal defects effectively, leading to missed issues, low efficiency, and high maintenance costs. Infrared thermal imaging technology addresses these challenges by providing non-contact, real-time, and accurate diagnostics for various power industry applications.
Coal Storage Monitoring
Infrared thermal imaging systems provide 24/7 monitoring of coal pile surface temperatures in open or semi-enclosed coal yards. By detecting temperature changes caused by heat accumulation, the system enables early warnings and remote alarms, allowing on-site personnel to handle abnormal areas promptly. This helps prevent coal pile self-ignition and mitigates potential safety risks.
Transmission Belt Monitoring
Long-distance, high-speed coal transmission belts are prone to issues such as foreign objects, misalignment, and tears, which can result in severe economic losses or accidents. Infrared systems integrate multiple modules for detecting misalignment, tears, foreign objects, and overheating. These systems provide real-time diagnostics and early warnings, reducing downtime and preventing costly failures.

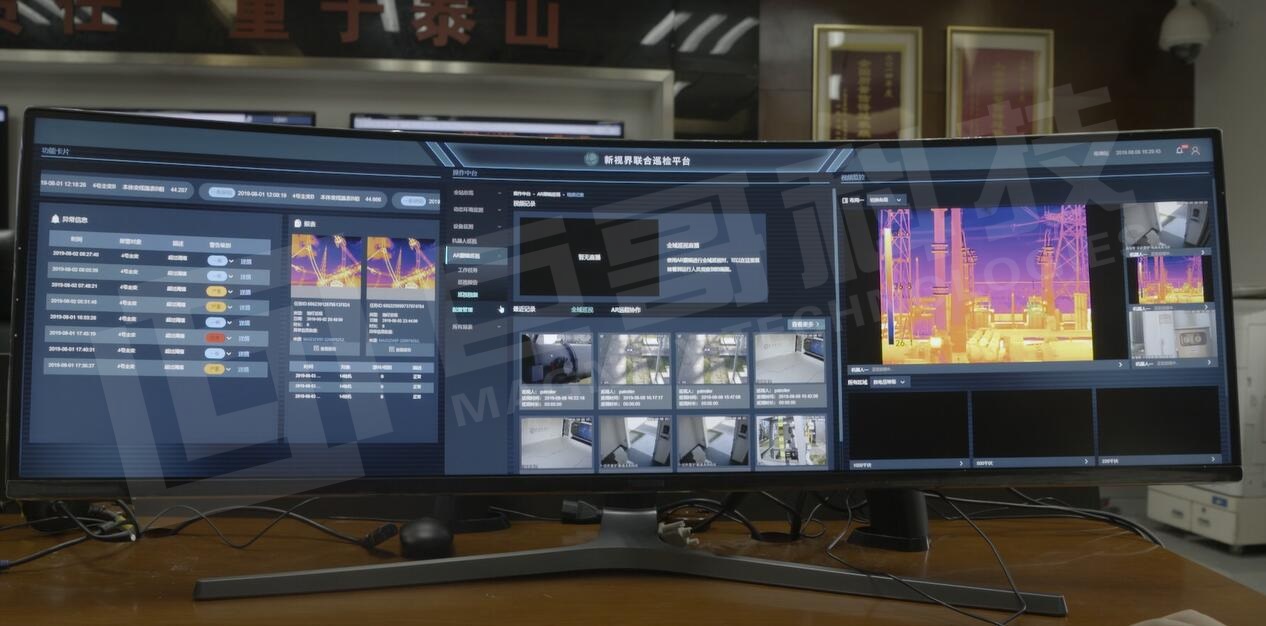
Equipment Status Monitoring
Infrared thermal imaging is used for real-time monitoring of critical equipment in power plants. The system detects temperature anomalies and generates alarms for abnormal conditions, allowing operators to address issues proactively. This 24/7 monitoring ensures continuous operation and minimizes the risk of equipment failure.
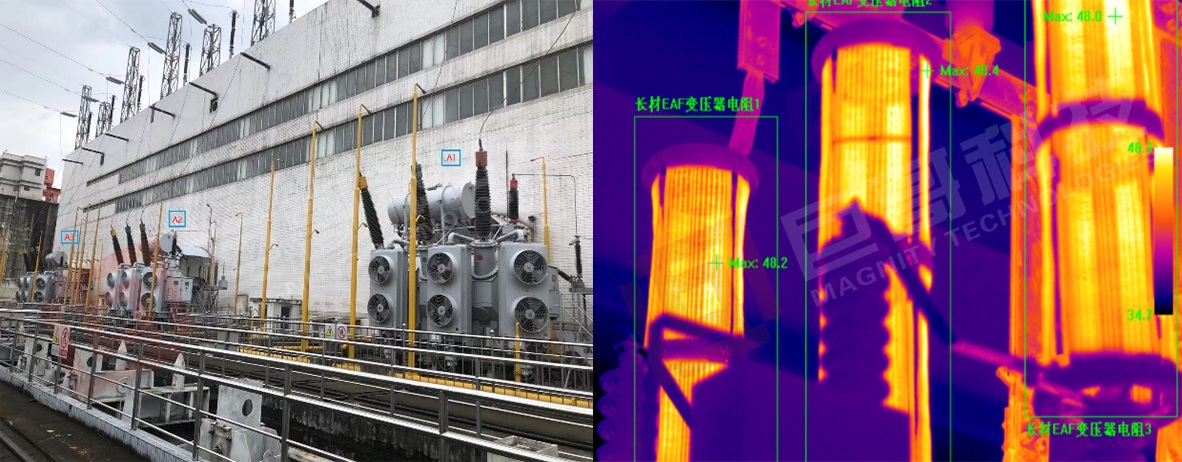

Hydropower Applications
In hydropower stations, large high-voltage electrical equipment requires temperature monitoring. Portable infrared imagers are labor-intensive and lack continuous data. Infrared online temperature monitoring provides continuous and real-time insights, preventing potential failures such as carbon brush overheating or abnormal wear on slip rings.
Wind Power Applications
Wind turbines operate under high load conditions, often experiencing generator or gearbox overheating. Infrared thermal imaging allows real-time monitoring of internal components, identifying abnormal temperature patterns and ensuring timely maintenance. This prevents equipment damage and enhances operational reliability.

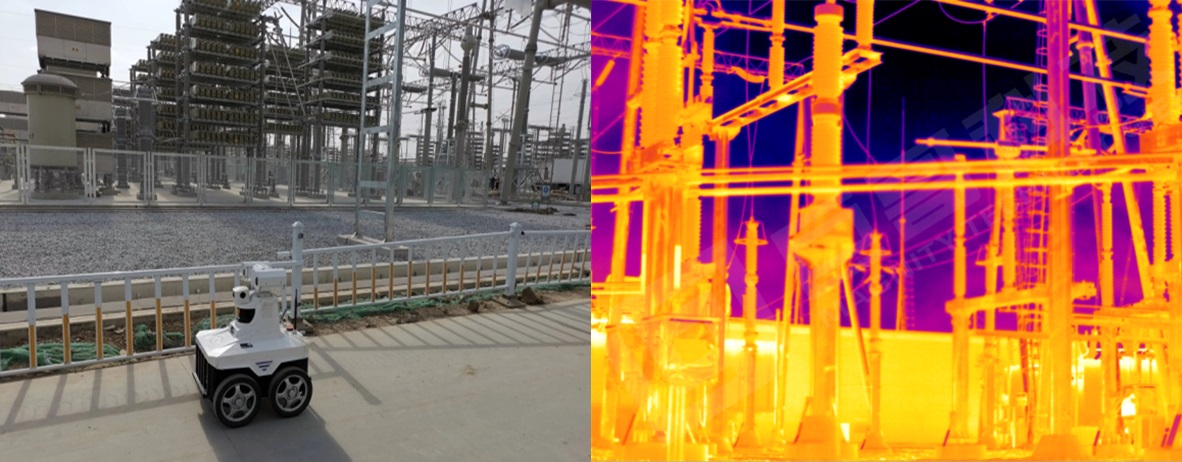
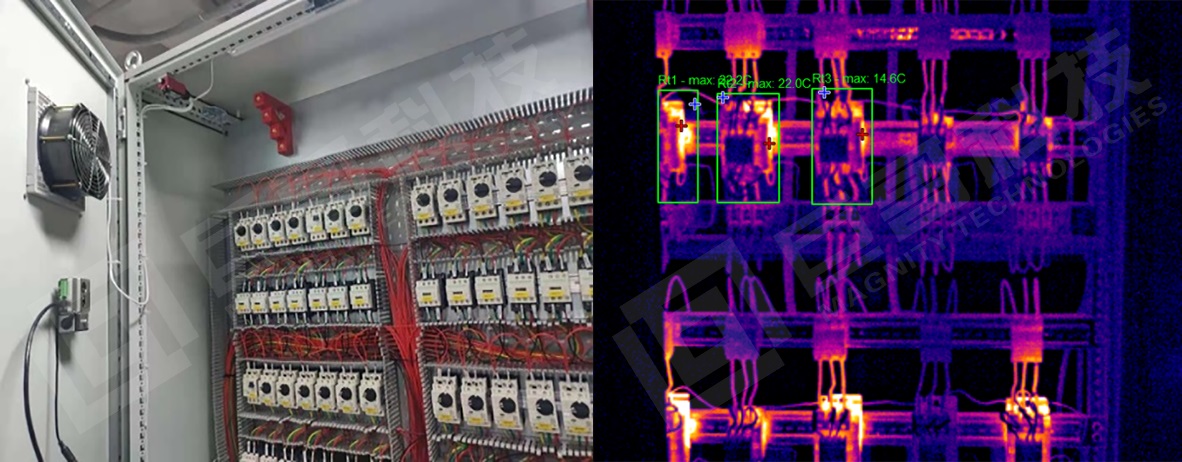
Substation Monitoring
Substations require precise inspection to prevent faults that can disrupt the entire system. Infrared thermal imaging enables comprehensive, non-contact monitoring, transforming traditional reactive maintenance into predictive maintenance. This significantly reduces workload and enhances system reliability.
